Open interest is a crucial concept for traders navigating the world of futures and options. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding open interest can enhance your trading strategy and decision-making. In this post, we'll explain what open interest is, how it works, and provide a numeric example to illustrate its significance.
What is Open Interest?
Open interest (OI) refers to the total number of outstanding derivative contracts, such as options and futures, that have not been settled. Unlike trading volume, which counts the number of contracts traded during a specific period, open interest measures the total number of contracts that are still active in the market.
Key Points to Remember:
- Open interest includes all active contracts that have not been closed, expired, or exercised.
- Increasing open interest typically indicates new money flowing into the market, signaling bullish sentiment, while decreasing open interest suggests that traders are closing positions, often indicating bearish sentiment.
Numeric Example of Open Interest
Let’s consider a simple example of trading activity over a few days to illustrate how open interest changes:
| Date | Trading Activity | Open Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Jan 1 | Trader A buys 1 option from Trader B | 1 |
| Jan 2 | Trader C buys 5 options from Trader D | 6 |
| Jan 3 | Trader A sells 1 option to Trader D | 5 |
| Jan 4 | Trader E buys 5 options from Trader C | 5 |
- Jan 1: Trader A purchases 1 option from Trader B, resulting in an open interest of 1.
- Jan 2: Trader C enters the market by buying 5 options from Trader D, increasing the open interest to 6.
- Jan 3: Trader A sells 1 option to Trader D to close a position. The open interest decreases to 5.
- Jan 4: Trader E buys 5 options from Trader C, keeping the open interest stable at 5.
This example shows how open interest fluctuates based on trading activity. The moves in open interest can provide insights into market liquidity and trader sentiment.
The Importance of Open Interest
- Liquidity Indicator: High open interest suggests a liquid market, making it easier for traders to enter and exit positions.
- Trending Insights: Rising open interest is often viewed as a potential confirmation of current trends, signaling that the market may continue its movement in the existing direction.
- Closing Positions: A decline in open interest indicates more positions are being closed than opened, possibly suggesting a reversal or weakening trend.
Trading Signals Based on Open Interest
Understanding how to interpret open interest can provide valuable trading signals. Here’s a breakdown of crucial signals related to market behaviors:
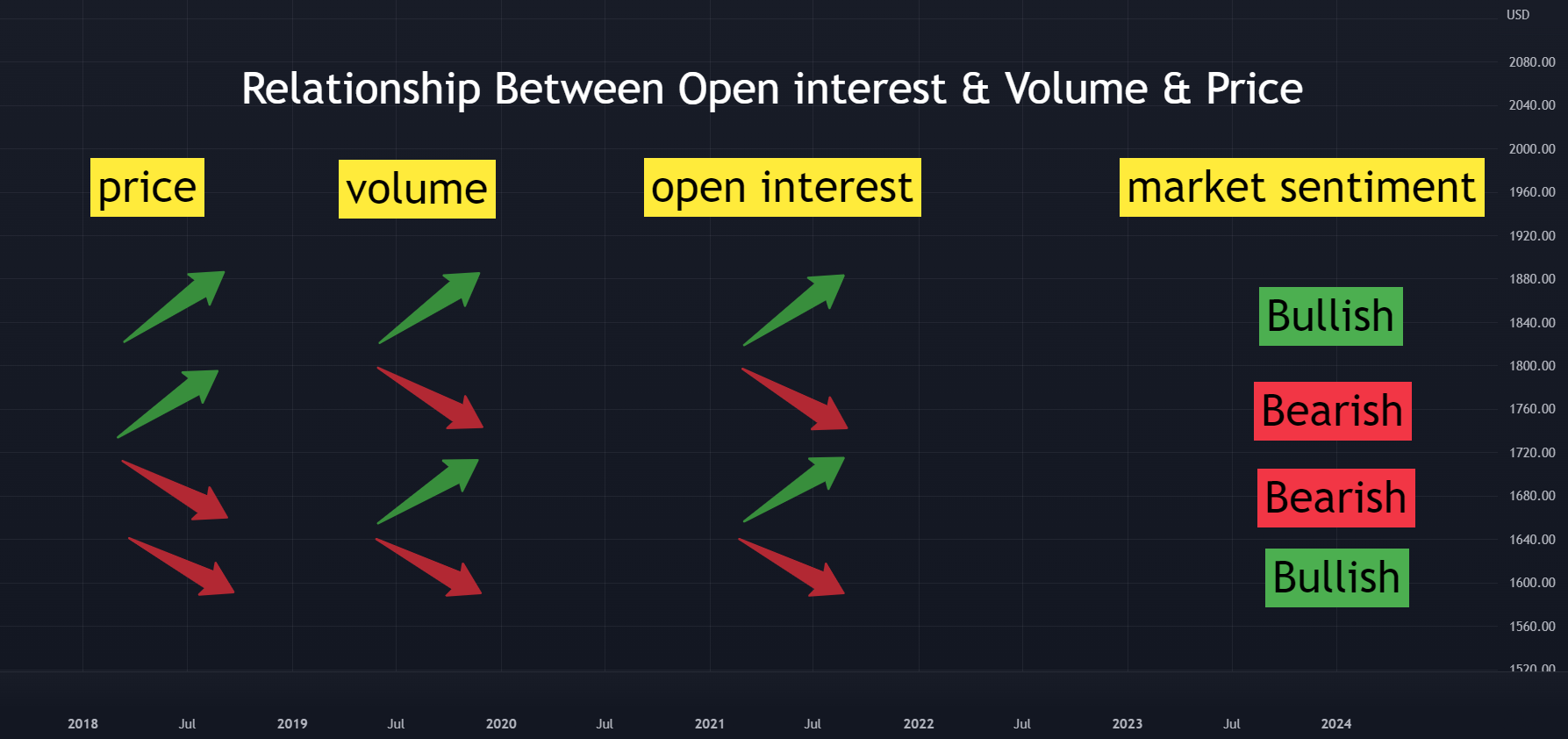
1. Bullish Signals
- Increasing Open Interest in a Rising Market: This indicates that new money is entering the market, suggesting bullish sentiment. Traders are adding positions in anticipation of further price increases.
- Declining Open Interest in a Falling Market: This may signal that long positions are being closed, suggesting that the market could be nearing a bottom, potentially leading to a reversal.
2. Bearish Signals
- Declining Open Interest in a Rising Market: This indicates that bullish positions are being closed and could suggest a weakening trend, signaling potential downward pressure.
- Increasing Open Interest in a Falling Market: This suggests that new short positions are being established, indicating bearish sentiment as traders anticipate further price declines.
Summary of Key Signals
| Market | Open Interest | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| rising | increasing | bullish signal: new money entering the market |
| rising | declining | bearish signal: closing of bullish positions |
| falling | increasing | bearish signal: new short positions being established |
| falling | declining | bullish signal: potential reversal as long positions close |
Conclusion
Understanding open interest is vital for traders aiming to enhance their trading strategies. By keeping an eye on open interest levels alongside price movements, traders can gain a clearer picture of market sentiment and liquidity. Whether you're trading options or futures, incorporating open interest analysis into your strategy can lead to more informed trading decisions.