In the world of trading and investment, forward and futures contracts play a crucial role in managing risk and speculating on the future prices of assets. If you're new to these concepts, don't worry! This blog post will break down the basics of forward and futures contracts in an easy-to-understand manner.
What Are Forward Contracts?
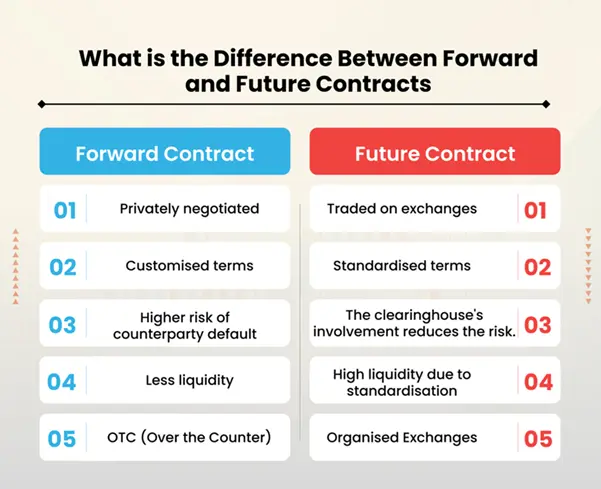
A forward contract is a private agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date. These contracts are customizable, meaning the terms can be tailored to fit the needs of both parties.
Key Features of Forward Contracts:
- Customization: Terms, including price and delivery date, can be adjusted.
- Counterparty Risk: Since these contracts are private, they carry risk if one party defaults.
- Settlement: Typically settled at the end of the contract term.
Example of a Forward Contract:
Imagine a farmer who grows wheat. If the current market price is $5 per bushel, the farmer can agree to sell 1,000 bushels to a buyer for $5.50 per bushel in six months. This agreement ensures that the farmer knows exactly how much he will earn, regardless of market fluctuations.
What Are Futures Contracts?
A futures contract is similar to a forward contract but is standardized and traded on exchanges. This standardization means that futures contracts have specific terms, such as contract size, expiration date, and settlement procedures, making them more accessible and liquid.
Key Features of Futures Contracts:
- Standardization: Terms are set by the exchange, enhancing liquidity.
- Reduced Counterparty Risk: Exchanges provide a clearinghouse to mitigate default risk.
- Daily Settlements: Futures are marked to market daily, adjusting prices based on market conditions.
Example of a Futures Contract:
Suppose a trader believes that the price of oil, currently at $70 per barrel, will rise. They buy a futures contract agreeing to purchase 100 barrels at this price. If the price climbs to $75 by the contract's expiration, the trader can sell the contract for a profit.
Why Use Forward and Futures Contracts?
Both forward and futures contracts are valuable tools for hedging against price fluctuations and speculating on price movements. They allow investors to lock in prices, manage risks, and potentially leverage their investments.
When to Use Them:
- Hedging: Businesses can protect against price volatility.
- Speculation: Traders can profit from anticipated price changes.
Conclusion
Understanding forward and futures contracts is essential for anyone looking to delve into trading and investment. These financial instruments provide opportunities for risk management and speculation, making them integral to modern financial markets.