Centralized organizations have led the way for the development and expansion of the internet over the past two decades. Decentralization is a hot topic in the tech industry right now as the internet evolves into Web 3.0. The topic of how organizations will look in the future within the context of a decentralized internet comes in the midst of these conversations. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAO), might be the way businesses operate in the future.
What are DAOs?
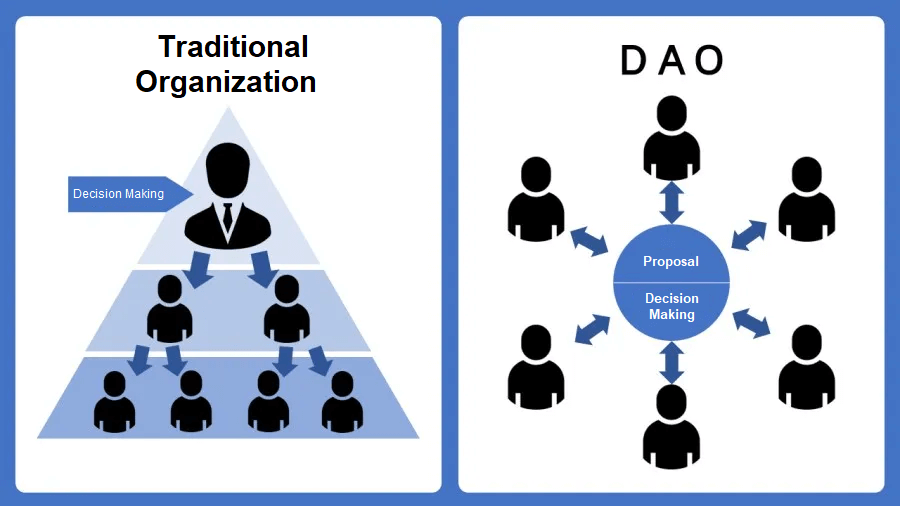
Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO), is a type of organization that operates without the need for centralized control. They are basically as a digitally native group owned and managed by like–minded individuals collaborating and coordinating together, governed by a set of rules encoded in smart contracts on a blockchain, for a specific purpose. This allows for greater transparency, security, and autonomy in decision-making processes, as well as increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness. DAOs have been used for a variety of purposes, including managing decentralized finance protocols, creating digital art, and running open-source software projects.
Background
The concept of DAOs emerged in 2013, when a group of individuals proposed a decentralized crowdfunding platform called "The DAO" (short for Decentralized Autonomous Organization). The DAO was designed to be a new type of investment fund, where investors could vote on proposals and decisions using blockchain technology. In 2016, The DAO raised over $150 million in an initial coin offering (ICO), making it the largest crowdfunded project at the time.
However, The DAO was later compromised by a hacker, who exploited a vulnerability in the smart contracts and siphoned off millions of dollars worth of Ether. This led to a contentious hard fork of the Ethereum network, with some members of the community supporting a rollback of the blockchain to recover the stolen funds, while others argued that this went against the principles of decentralization and immutability.
Despite the controversy surrounding The DAO, the concept of DAOs continued to gain traction, with numerous projects and platforms being developed in the years following. Today, DAOs are seen as a promising tool for decentralized governance and decision-making, with potential applications in fields such as finance, art, gaming, and more.
Characteristics of DAOs
DAOs differ from traditional organizations in a number of ways:
| DAO | Traditional Organization |
|---|---|
| Usually flat, and fully democratized | Usually hierachical |
| Voting required by members for any changes to be implemented | Depending on structure, changes can be demanded from a sole party, or voting may be offered |
| Votes tallied, and outcome implemented automatically without trusted intermediary | if voting allowed, votes are tallied internally, and outcome of voting must be handled manually |
| Services offered are handled automatically in a decentralized manner (for example distribution of philanthropic funds) | Requires human handling, or centrally controlled automation, prone to manupulation |
| All activitiy is transparent and fully public | Activity is typically private, and limited to the public |
Different types of DAOs
There are different types of DAOs, each with its own unique characteristics and goals. Some of the most common types include:
- Investment DAOs: These are DAOs that manage investment funds, allowing members to pool their resources and make collective investment decisions.
- Service DAOs: These are DAOs that provide a specific service or product, such as digital art, gaming, or social media.
- Governance DAOs: These are DAOs that focus on decentralized governance, allowing members to propose and vote on changes to the organization's rules or policies.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) DAOs: These are DAOs that operate within the decentralized finance ecosystem, providing financial services such as lending, borrowing, and trading.
- Social DAOs: These are DAOs that focus on creating social impact or promoting specific causes, such as environmental sustainability, education, or social justice.
- Research DAOs: These are DAOs that focus on research and development in a specific field, such as science, technology, or medicine.


DAO memberships
There are different types of DAO memberships, each with its own set of rights and responsibilities. Some of the most common types include:
- Token holders: These are members who own tokens that represent a stake in the DAO. Token holders may have the right to vote on proposals, receive rewards or dividends, or participate in other aspects of the DAO's decision-making process.
- Contributors: These are members who contribute to the DAO in some way, such as by providing work, services, or resources. Contributors may be compensated in tokens, rewards, or other forms of value.
- Curators: These are members who are responsible for managing the DAO's content or assets, such as in a digital art or gaming DAO.
- Validators: These are members who are responsible for validating transactions on the DAO's blockchain, typically in a proof-of-stake or proof-of-work consensus model.
- Core team members: These are members who are responsible for managing the day-to-day operations of the DAO, such as in a governance or service DAO.
- Advisors: These are members who provide guidance or expertise to the DAO, such as in a research or social DAO.
Why are DAOs important?
DAOs are important for a number of reasons:
- Decentralization: DAOs represent a shift away from traditional, centralized organizational structures, promoting greater autonomy, transparency, and efficiency.
- Innovation: DAOs enable new forms of collaboration and value creation, unlocking new opportunities for innovation and experimentation.
- Community: DAOs are often built around shared interests or values, creating tight-knit communities of like-minded individuals who can work together to achieve common goals.
- Trust: By operating on a public blockchain and using transparent, rules-based decision-making processes, DAOs build trust among their members and promote accountability.
- Inclusivity: DAOs are open to anyone with an internet connection, providing a level playing field for participation and minimizing barriers to entry.
Challenges & Limitations
While DAOs offer a number of potential advantages, there are also several challenges and limitations to consider:
- Technical complexity: Building and operating a DAO can be technically complex, requiring expertise in blockchain development, smart contract design, and decentralized governance.
- Legal and regulatory issues: The legal and regulatory framework for DAOs is still evolving, and there may be uncertainty around how they are treated under existing laws and regulations.
- Governance challenges: DAOs rely on decentralized decision-making processes, which can be difficult to manage and coordinate effectively. There may be challenges around reaching consensus, managing conflicts, and ensuring that decisions are made fairly and transparently.
- Security risks: DAOs are vulnerable to cyber attacks and hacking attempts, particularly if they are not properly designed and secured.
- Adoption barriers: Despite their potential benefits, DAOs may face adoption barriers, particularly if they are unfamiliar or difficult to use for non-technical users.
Summary
DAOs represent a new paradigm in organizational design, governance, and decision-making, opening up new possibilities for collaboration, innovation, and community-building. However, the concept of DAOs will need to continue to evolve and mature, with ongoing research and development focused on improving their security, usability, and governance structures. Additionally, collaboration between developers, legal experts, and policymakers will be necessary to ensure that DAOs are able to operate safely, securely, and within the bounds of applicable laws and regulations.